Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers or nodes in a network. It was originally introduced as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin but has since found applications in various industries beyond finance.
At its core, a blockchain is a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. These transactions are verified and added to the block through a process called consensus, which involves the agreement of multiple participants or nodes in the network. Once a block is added to the chain, it is difficult to alter or tamper with the data contained within it due to cryptographic hashing and the distributed nature of the network.
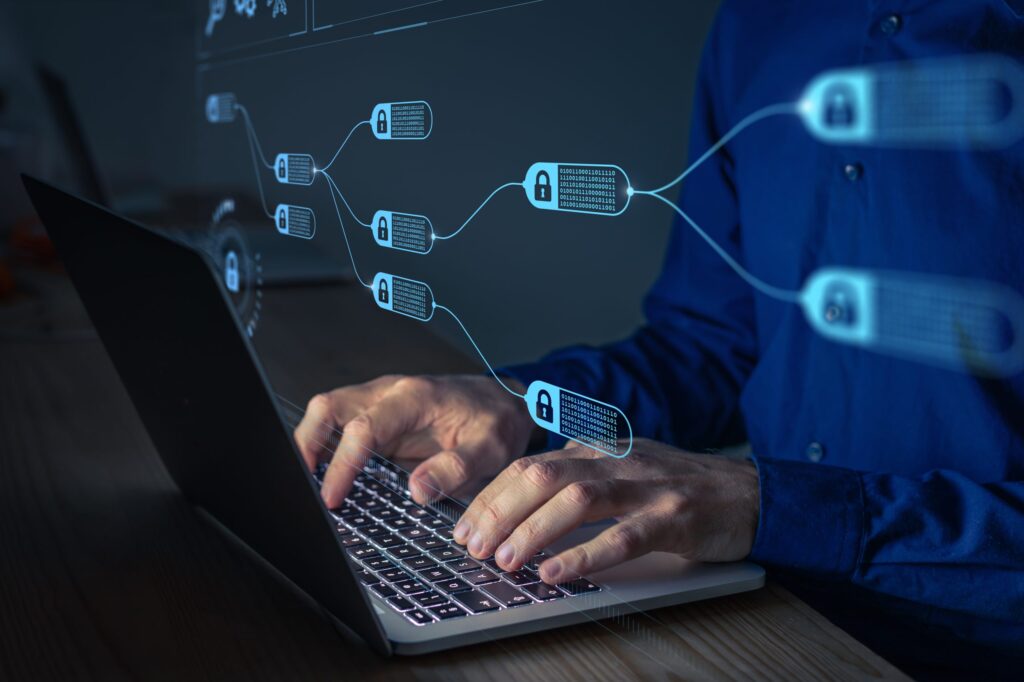

Key characteristics of blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, meaning there is no central authority controlling the entire system. Instead, multiple participants (nodes) maintain and validate the blockchain.
- Transparency: The blockchain ledger is typically open and transparent, allowing all participants to view the transaction history. This transparency enhances trust and accountability in the system.
- Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure and verify transactions. Each block contains a unique hash, and any attempt to modify a block will require the alteration of subsequent blocks, making it highly resistant to tampering.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is difficult to change or delete. This immutability ensures the integrity of the data and prevents fraudulent activities.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain can support the execution of self-executing contracts known as smart contracts. Smart contracts automatically enforce the terms and conditions of an agreement, eliminating the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency.
Blockchain technology has applications beyond cryptocurrencies. It can be utilized in supply chain management, healthcare, voting systems, identity verification, asset ownership, and more, where transparency, security, and trust are crucial. However, it’s important to note that while blockchain offers many benefits, it also has limitations, including scalability, energy consumption, and regulatory challenges that need to be addressed for wider adoption in certain industries.
























+ There are no comments
Add yours