Increase Vitamin B12 Levels Naturally: Practical Methods and Tips
Maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin B12 is essential for overall health and well-being. If you’re looking to naturally boost your Vitamin B12 levels, this guide will provide you with valuable insights and practical tips to ensure your nutritional health.
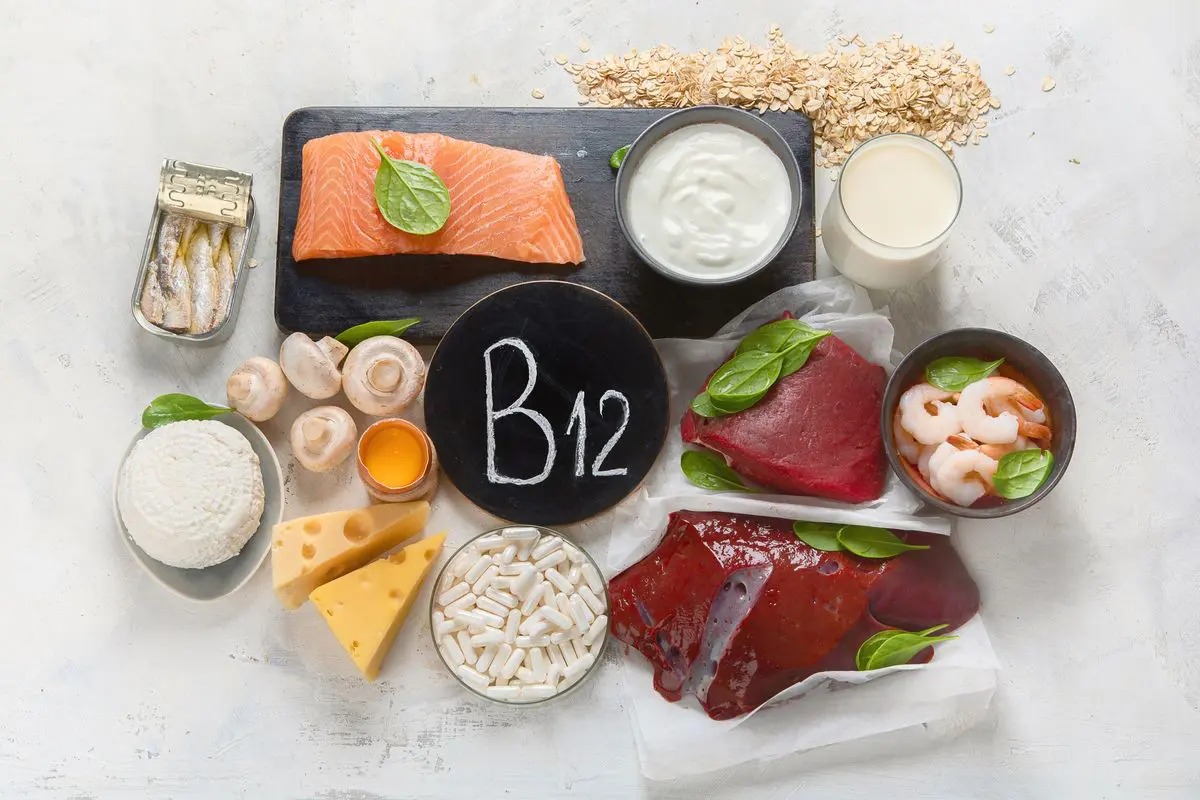

What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including nerve function, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell production. A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, fatigue, and neurological issues.
Step 1: Consume B12-Rich Foods
- Animal Products: Include foods like lean meats, poultry, fish, and eggs in your diet. These are some of the best sources of Vitamin B12.
- Dairy and Dairy Alternatives: Opt for milk, cheese, and yogurt, or their plant-based counterparts fortified with Vitamin B12.
- Fortified Foods: Many cereals, plant-based milk, and nutritional yeast products are fortified with Vitamin B12.
Step 2: Incorporate Seafood
- Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, trout, and sardines are excellent sources of Vitamin B12.
- Shellfish: Shellfish such as clams, mussels, and crabs are rich in Vitamin B12.
Step 3: Include Poultry
- Chicken: Skinless chicken breast is a lean source of Vitamin B12.
- Turkey: Turkey meat, especially the white meat, is also a good source.
Step 4: Opt for Lean Meats
- Beef: Choose lean cuts of beef like sirloin or tenderloin to boost your Vitamin B12 intake.
- Pork: Lean cuts of pork, such as loin chops, provide a good amount of Vitamin B12.
Step 5: Add Eggs to Your Diet
- Whole Eggs: Eggs, especially the yolk, are a natural source of Vitamin B12.
Step 6: Embrace Plant-Based Options
- Nutritional Yeast: This yeast is often fortified with Vitamin B12 and can be used to add a cheesy flavor to dishes.
- Fortified Plant-Based Foods: Incorporate fortified plant-based milk, cereals, and meat alternatives into your diet.
Step 7: Pay Attention to Absorption
- Stomach Acid: Adequate stomach acid is required for Vitamin B12 absorption. Certain medical conditions can affect acid production.
- Intrinsic Factor: Vitamin B12 absorption also depends on intrinsic factor, a protein produced in the stomach. Some medical conditions can interfere with its production.
Step 8: Consult a Healthcare Professional
- Blood Tests: If you suspect a Vitamin B12 deficiency, consult a healthcare professional for a blood test to determine your levels.
- Supplementation: Depending on your levels and health condition, your doctor may recommend Vitamin B12 supplements.
By incorporating Vitamin B12-rich foods into your diet and paying attention to absorption factors, you can naturally enhance your Vitamin B12 levels and enjoy improved health and vitality. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on your individual needs.






















+ There are no comments
Add yours